[JAVA] 자바 직렬화(serialize) 개념과 주의할 점
개념
- 자바 직렬화란 자바 시스템 내부에서 사용되는 객체 또는 데이터를 외부의 자바 시스템에서도 사용할 수 있도록 바이트(byte) 형태로 데이터 변환하는 기술과 바이트로 변환된 데이터를 다시 객체로 변환하는 기술(역직렬화)을 아울러서 이야기한다.
- 시스템적으로 이야기하자면 JVM(Java Virtual Machine 이하 JVM)의 메모리에 상주(힙 또는 스택)되어 있는 객체 데이터를 바이트 형태로 변환하는 기술과 직렬화된 바이트 형태의 데이터를 객체로 변환해서 JVM으로 상주시키는 형태를 같이 이야기한다.
- 자바 직렬화 형태의 데이터 교환은 자바 시스템 간의 데이터 교환을 위해서 존재한다.
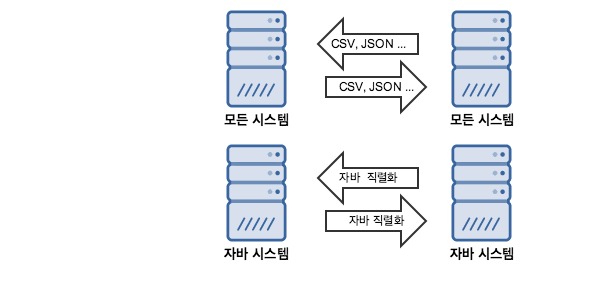
- 자바 기본(primitive) 타입과 java.io.Serializable 인터페이스를 상속받은 객체는 직렬화 할 수 있는 기본 조건을 가집니다.
기본 개념 출처: http://woowabros.github.io/experience/2017/10/17/java-serialize.html
주의할 점(사실 요게 메인 ㅎㅎ):
1. 자바 직렬화가 필요한 경우 subList를 사용하지 말자!(캐시에서도 자바 직렬화가 필요한 경우가 있을 수 있다!)
- subList를 사용한 경우
@Test(expected = NotSerializableException.class)
public void ArrayList_subList_테스트() throws IOException {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("홍");
list.add("성");
list.add("민");
list = list.subList(0, 2);
byte[] bytes = pickle(list); //occur error!
}
@Test(expected = NotSerializableException.class)
public void Arrays_asList_subList_테스트() throws IOException {
String[] array = new String[3];
array[0] = "홍";
array[1] = "성";
array[2] = "민";
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(array);
list = list.subList(0, 2);
byte[] bytes = pickle(list); //occur error!
}
@Test(expected = NotSerializableException.class)
public void LinkedList_subList_테스트() throws IOException {
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add("홍");
list.add("성");
list.add("민");
list = list.subList(0, 2);
byte[] bytes = pickle(list); //occur error!
}
@Test(expected = NotSerializableException.class)
public void Vector_subList_테스트() throws IOException {
List<String> list = new Vector<>();
list.add("홍");
list.add("성");
list.add("민");
list = list.subList(0, 2);
byte[] bytes = pickle(list); //occur error!
}
private <T> byte[] pickle(T obj) throws IOException {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
return baos.toByteArray();
}
- AbstractList내 subList를 통해 RandomAccessSubList 혹은 SubList가 생성된다.
- Vector와 ArrayList는 subList메서드를 재 구현 했지만 결과적으로 반환형으로 SubList를 직접 반환하거나 랩핑해서 반환한다.
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return (this instanceof RandomAccess ?
new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex) :
new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex));
}
- 하지만 RandomAccessSubList와 SubList에는 직렬화 인터페이스를 구현하지 않았다.
class RandomAccessSubList<E> extends SubList<E> implements RandomAccess {
RandomAccessSubList(AbstractList<E> list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
super(list, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
}
class SubList<E> extends AbstractList<E> {
private final AbstractList<E> l;
private final int offset;
private int size;
SubList(AbstractList<E> list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex);
if (toIndex > list.size())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex);
if (fromIndex > toIndex)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex +
") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
l = list;
offset = fromIndex;
size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = l.modCount;
//중략...
}
- 이로 인해 직렬화 에러가 발생하게 된다.
- 추가적으로 SubList 클래스처럼 실제 List를 만들지 않고 단순히 전달 받은 list를 참조하고 offset과 size를 저장하는 식의 방식으로 구현한 클래스(view용 collection)들이 있다. 만약 파라메터로 전달 받은 실제 list가 변경되는 경우 문제가 생길 수 있으니 이 점도 주의하자.
Exception in thread "main" java.io.NotSerializableException: java.util.RandomAccessSubList
- 만약 직렬화를 할 대상 리스트가 subList 반환한 결과인 경우 ArrayList로 감싸서 사용해야 한다.
list = new ArrayList<>(list.subList(0, 2));
- ArrayList의 생성자에 컬렉션을 구현한 인스턴스를 넘길 경우 copyOf를 통해 깊은 복사를 한다. 또한 java.io.Serializable를 implements 하고 있기 때문에 직렬화가 가능하다.
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
2. 추가적으로 Iterables.partition(final Iterable iterable, final int size)는 자바 직렬화가 필요한 경우 절대 사용하면 안된다!
- Iterators에서 내부 적으로 마지막 리스트의 크기가 원하는 갯수 미만으로 떨어지는 경우 subList가 호출된다.
- subList에 직렬화 인터페이스가 없어 문제가 발생하지만 별 다른 설명이 없다. 문제가 있는 자바 라이브러리라고 볼 수 있다.
// Iterators.java
private static <T> UnmodifiableIterator<List<T>> partitionImpl(
final Iterator<T> iterator, final int size, final boolean pad) {
checkNotNull(iterator);
checkArgument(size > 0);
return new UnmodifiableIterator<List<T>>() {
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return iterator.hasNext();
}
@Override
public List<T> next() {
if (!hasNext()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
Object[] array = new Object[size];
int count = 0;
for (; count < size && iterator.hasNext(); count++) {
array[count] = iterator.next();
}
for (int i = count; i < size; i++) {
array[i] = null; // for GWT
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // we only put Ts in it
List<T> list = Collections.unmodifiableList((List<T>) Arrays.asList(array));
return (pad || count == size) ? list : list.subList(0, count); //여기서 문제가 발생할 여지가 있다!
}
};
}
- 위 list.subList(0, count)가 호출되면
- Collections내 UnmodifiableRandomAccessList의 subList가 호출된다.
/**
* @serial include
*/
static class UnmodifiableRandomAccessList<E> extends UnmodifiableList<E>
implements RandomAccess
{
UnmodifiableRandomAccessList(List<? extends E> list) {
super(list);
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return new UnmodifiableRandomAccessList<>(
list.subList(fromIndex, toIndex)); //여기가 실행되고
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2542308836966382001L;
/**
* Allows instances to be deserialized in pre-1.4 JREs (which do
* not have UnmodifiableRandomAccessList). UnmodifiableList has
* a readResolve method that inverts this transformation upon
* deserialization.
*/
private Object writeReplace() {
return new UnmodifiableList<>(list);
}
}
- AbstractList내 subList를 통해 RandomAccessSubList가 생성된다.
- 생성된 RandomAccessSubList는 UnmodifiableRandomAccessList의 생성자로 전달된다.
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return (this instanceof RandomAccess ?
new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex) :
new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex));
}
- 결과적으로 UnmodifiableRandomAccessList의 부모 클래스인 UnmodifiableList에 있는 list 필드에 RandomAccessSubList가 저장된다.
- 하지만 ArrayList 생성자와 다르게 UnmodifiableRandomAccessList 생성자에 리스트를 넘긴 경우 깊은 복사를 하지 않는다. 얕은 복사로 단지 래핑만을 한다.
static class UnmodifiableList<E> extends UnmodifiableCollection<E>
implements List<E> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -283967356065247728L;
final List<? extends E> list;
//..중략
}
- 마찬가지로 RandomAccessSubList에는 직렬화 인터페이스가 구현되지 않았다.
- 이로 인해 직렬화 예외가 발생하게 된다.
class RandomAccessSubList<E> extends SubList<E> implements RandomAccess {
RandomAccessSubList(AbstractList<E> list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
super(list, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
}

Comments